With increasing scale, it becomes more challenging to effectively manage ecommerce store operations. Keeping up with the warehousing and inventory management demands can quickly become overwhelming as your business grows. But the right internal systems can make this easier. The use of SKUs for ecommerce is one such system.
Stock keeping units (SKUs) can make it significantly easier for ecommerce businesses to manage shipping orders, replenish dwindling stock, and avoid errors and mistakes that lead to bad customer experiences.
What is an SKU?
An SKU is an alphanumeric code that’s used to distinguish products from each other in an ecommerce system.
Features of the products, such as brand, category, color, size, etc, are used to determine individual attributes that make up each element of the SKU code. The information is in decreasing order of importance.
For example, an SKU number for a green shirt by Marks & Spencer in a small size could be MS-SH-GR-S. Here, MS indicates the brand Marks & Spencer, SH stands for shirt, GR for the color green, and S is the size.
Are SKU and UPC the same?
SKUs and Universal Product Codes (UPCs) may erroneously be used as interchangeable terms, but these are different. 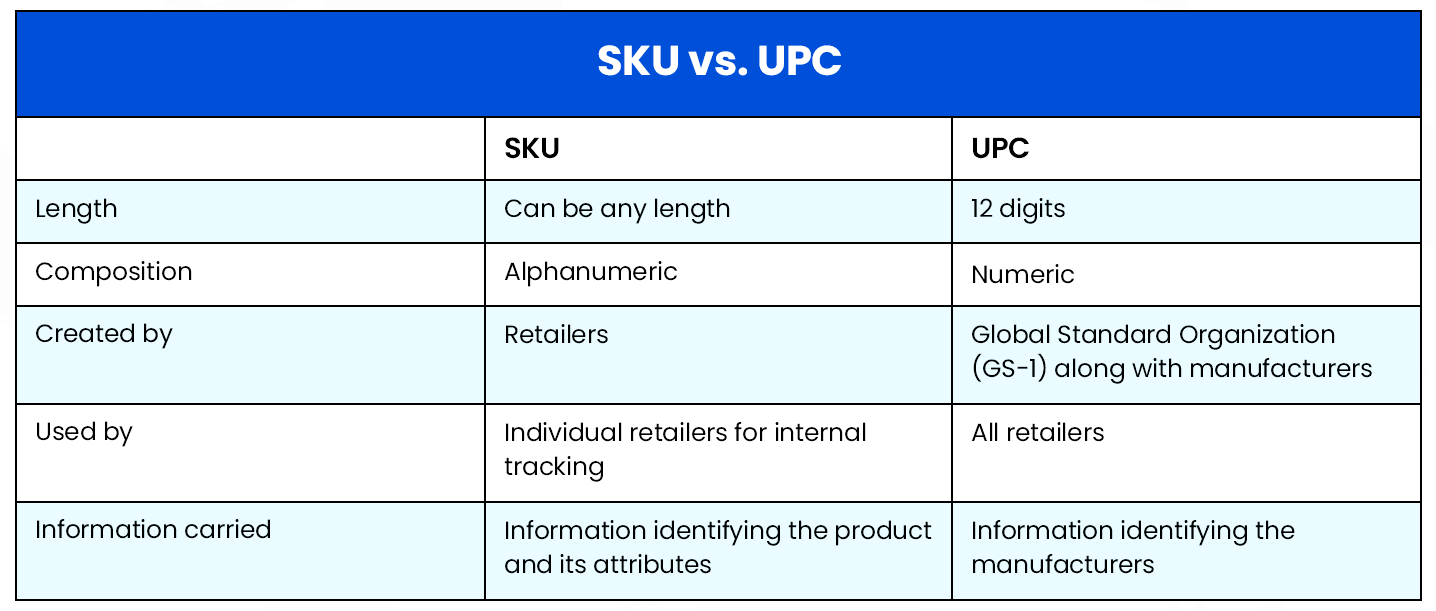
SKUs are generated and used internally within a company — so if two different ecommerce stores carried the same product, both would have a different SKU. UPC is a 12-digit number that remains the same for a single product regardless of the business that’s selling it or its location. A barcode is essentially a UPC rendered in a machine-readable format.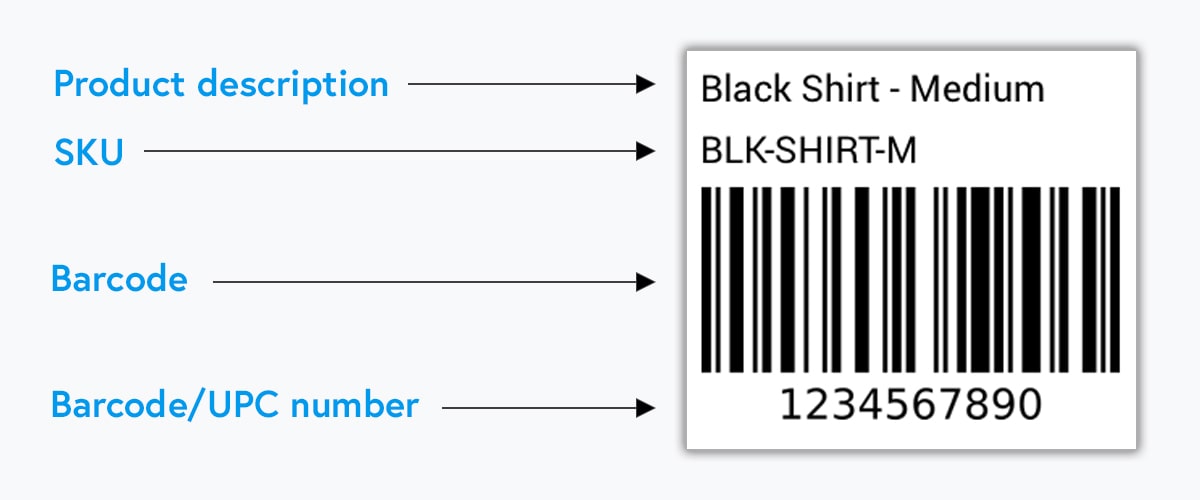
In its lifecycle, a product can have only one UPC but can have multiple SKUs.
Why do ecommerce businesses need SKUs?
SKUs are used to organize inventory. They make it possible to identify unique products and track them throughout their journey in the ecommerce system. They help you monitor inventory levels and replenish items that are running out of stock. 
SKUs also make it possible to organize your store layout or warehouse logically so that inventory can be located quickly and effortlessly. This helps move products faster and deliver better customer experiences.
Designing and optimizing SKUs is an especially critical part of multi-channel ecommerce operations.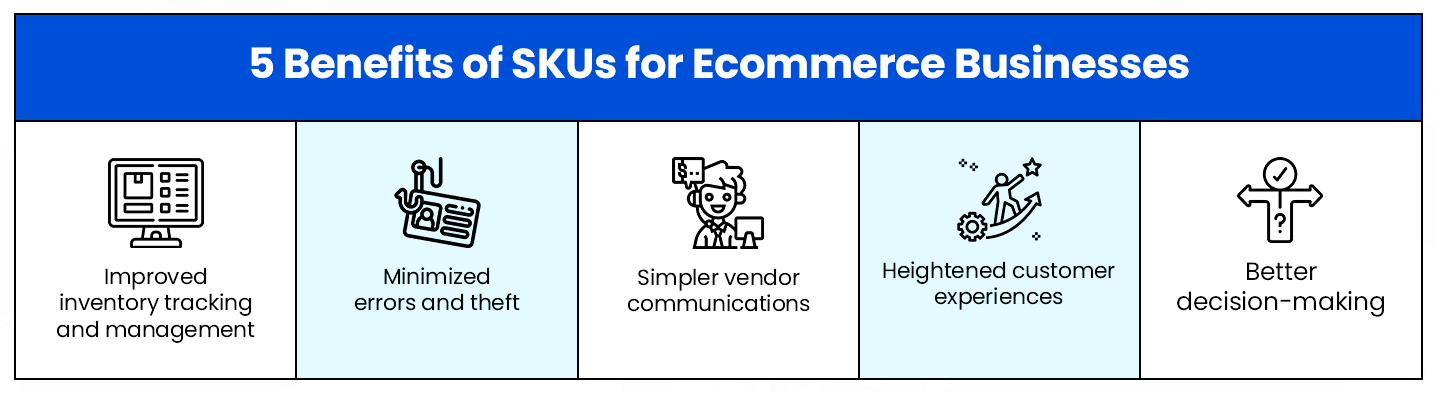
With an optimized SKU inventory management system, your business performs better. Here’s what this system does for your business.
1. Improved inventory tracking
Assigning a unique code to each product makes it easier for you to track inventory. SKUs contain a lot of meaningful information, which helps streamline your day-to-day operations.
With SKUs, you can search and reference products anywhere in your storage facilities. You can easily see how many products have been sold, how many products are available, and how many have gone out of stock. This helps save time and costs, and lets you manage your inventory more effectively.
Check out: BigCommerce Development
2. Minimized errors and theft
Using SKU codes, you can keep better track of overstock, manage inventory shipments more efficiently, perform spot checks to make sure inventory counts are accurate, and view reports by department.
All this makes it easy to ensure that inventory loss due to miscommunication, human error, and theft is minimized, and that correct orders are going out each time.
3. Simpler communication with vendors and third-party logistics providers
Well-designed SKU codes help to streamline communication with vendors and logistics partners.
As you scale up and start dealing with more vendors and 3PL providers, SKU codes help to minimize challenges with inventory tracking and ensure a smoother process.
4. Better customer experiences
By minimizing stockouts, ensuring that accurate inventory and pricing is always available, and making it easy to locate items, an optimized SKU system makes the shopping and checkout process frictionless for customers.
Read Next: How Experiential Data Can Help Create an Outstanding Customer Experience
5. Improved decision-making
By assigning SKU codes, you can keep better track of your inventory and make better merchandising decisions.
In this way, well-implemented SKU systems also help you capitalize on sales opportunities and increase your revenue.
How to create an effective SKU system
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to creating SKU codes.
You can create SKU codes in any way that works best for your business. But there are some important considerations in this process to ensure that the SKU codes generated can be easily understood and used by employees and vendors.
1. Define a format that’s right for your business
When creating an SKU format, keep in mind your specific business requirements and inventory management objectives. A format that works for another business might not be right for yours. For example, a retail business that’s distributed across multiple locations might find it necessary to include the location in the SKU code, while others may not.
However, make sure you include only as much information as necessary to avoid making your SKU codes too long.
Some of the attributes you might want to consider include:
- Store or location
- Department
- Category
- Subcategory
- Variants
2. Use a logical order of attributes
Begin your SKU code with high-level attributes (brand, category, location, etc.) and work down to more granular levels (size, color, style, etc.). 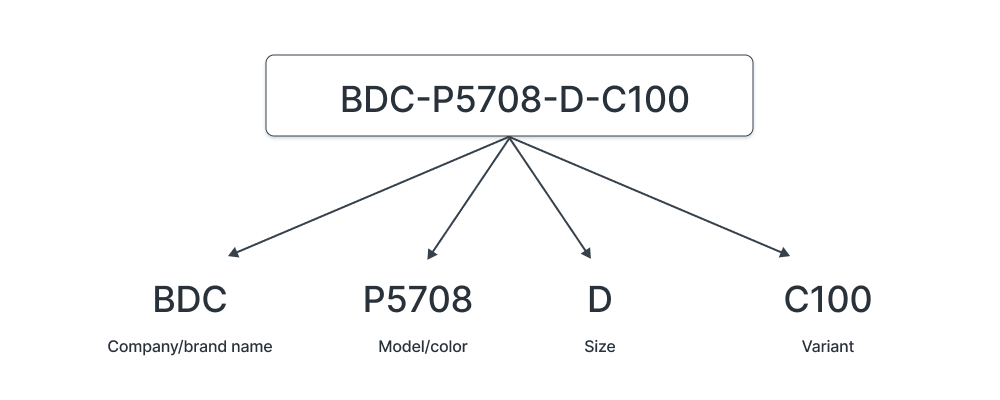
You may want to end with a sequential number that makes it easy to tell older items apart from newer ones.
3. Be careful about the characters you include
Use only alphanumeric characters, dashes (-) and underscores (_) while generating SKU codes. Avoid using special characters such as &, #, $, etc, as these can make your SKU codes hard to read and introduce errors when transferring them into different software programs.
Don’t start your SKU code with a zero. In some programs, a zero at the beginning could be disregarded and removed. Also, try not to use letters and numbers that can be confused for others, such as the numeral 0 and the letter O, as well as the lower case l, the upper case I, and the numeral 1.
4. Don’t settle for using manufacturer numbers
It might seem easier to just use the manufacturer numbers instead of designing your own SKU system, but this will not give you the same benefits as having SKUs that are designed for your specific business needs. Instead, create an SKU system tailored to your business and its inventory management needs.
SKUs for profitable growth
Prima facie, SKUs are just strings of alphabets and numbers on boxes. But that’s the genius of the system—it brings order to chaos without introducing complex processes that are self-defeating.
But the real value of SKUs is realized by enterprises that use the system for more than accurate inventory management. By embracing an SKU architecture, ecommerce businesses can forecast demand more accurately, amplify the biggest profit generators, increase sales even when products are out of stock, and generate memorable experiences for your customers.
Above all, enterprises can experience profitable growth and leave competitors behind!
Read Next: Ecommerce Development