The question is not whether your business experiences a disaster but when it is prepared to face it. Cybercrime, natural disasters, and hardware malfunctions are just a few increasing hazards for modern enterprises. According to Seagate, 140,000 hard drives malfunction in the US per week. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, a ransomware attack on a company will occur every 14 seconds, and with growing years, there will be one every 11 seconds. According to CNBC, the US suffered $91 billion in losses due to natural disasters. These numbers clearly show the importance of a solid backup and recovery plan.
Have you ever considered how downtime will affect your business when the time comes?
A reliable cloud consulting company can help you with a robust strategy to ensure backup and recovery. According to Gartner, a business’s average downtime costs $5,600 per minute or over $300,000 per hour. Considering this figure, it is evident that cyber attacks can cause significant harm to a company. And the effects go beyond money. Disasters also harm customer loyalty, company reputation, productivity, and morale for organizations that survive. This shows that businesses can’t afford to have downtime in the digital world. Now the question comes: How can you strategize a solid backup and recovery plan, and is there any way it can be done easily? The Cloud is considered the jack of all trades when it comes to backup and recovery. Let’s understand how your business can utilize the cloud for backup and recovery.
How does Cloud Backup & Recovery work?
Cloud backup stores data on remote servers, removing the need for physical storage infrastructure. This technique provides advantages such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and automated backups to preserve and restore data. Cloud disaster recovery aims to quickly restore critical services and data following a disaster or disruption. Cloud infrastructure helps reduce downtime, improve recovery time objectives (RTOs), and maintain business continuity. The cloud’s flexibility and architecture make it suitable for disaster recovery. Cloud backup is done in two ways:
-
Continuous Replication
The cloud provider copies your company’s data to its servers continuously as long as the data keeps changing. This is the most popular kind of cloud backup, which businesses utilize when they always need to maintain an updated copy of their data.
-
Scheduled Replication
Scheduled replication involves the cloud provider making scheduled copies of your company’s data. Businesses that don’t always need an updated copy of their data often use this.
Different Types Of Cloud Backup
There are various types of cloud backup options that businesses can use depending on their demands and requirements. Common types of cloud backup:
-
Full Backup
A full backup requires making a complete copy of all the files and data within the organization’s environment. It captures all data, including files, databases, apps, and system configurations. The goal of the backup procedures is to record any updates or modifications made since the last complete backup. Complete backups offer full data protection but might take a long time and use much storage space.
-
Incremental Backup
Incremental backups only record changes made to the data since the previous backup, whether a complete backup or another incremental backup. This method backs up modified or newly produced data, resulting in faster backup operations and lower storage requirements. However, complete data recovery may take longer because it requires restoring the most recent full backup and applying successive incremental backups.
-
Differential Backup
Differential backup records all changes to the data since the last complete backup. Unlike incremental backup, differential backup records change since the previous full backup. This strategy decreases the number of backup sets needed for data recovery, making restoring the most recent full backup and differential backup faster. As differential backups grow in size, they require additional storage space.
-
Continuous Data Protection (CDP)
Data backup in real-time is provided by Continuous Data Protection (CDP). Every modification to the data is recorded and replicated, guaranteeing that backups are always current. By continuously monitoring and backing up changes, CDP reduces the risk of data loss and offers a more precise recovery point objective (RPO). This approach is especially appropriate for businesses that need high availability and less data loss.
-
Snapshot Backup
Snapshot backup uses point-in-time snapshots to record the status of the data at a particular point in time. Making a replica of the data in its current condition enables organizations to return to that moment if needed. Regular intervals are usually utilized for taking snapshots, providing prompt data restoration to a particular point. However, snapshots are generally kept in the same cloud environment and cannot offer the same degree of data security as off-site backups.
-
Hybrid Backup
Hybrid backup integrates cloud and on-premises backup techniques. It offers the advantages of both methods by generating backups on-site and in the cloud. Cloud backup ensures off-site data protection and disaster recovery capabilities, while hybrid backup offers the benefit of quick local backup and recovery for instantaneous data restoration. Organizations can select the best kind of cloud backup Based on data volume, bandwidth availability, recovery needs, storage expenses, and preferred recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Various backup types may be used in numerous situations to create a thorough and effective backup plan.
To understand the cost of computing services, read this blog- Cloud Cost Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide.
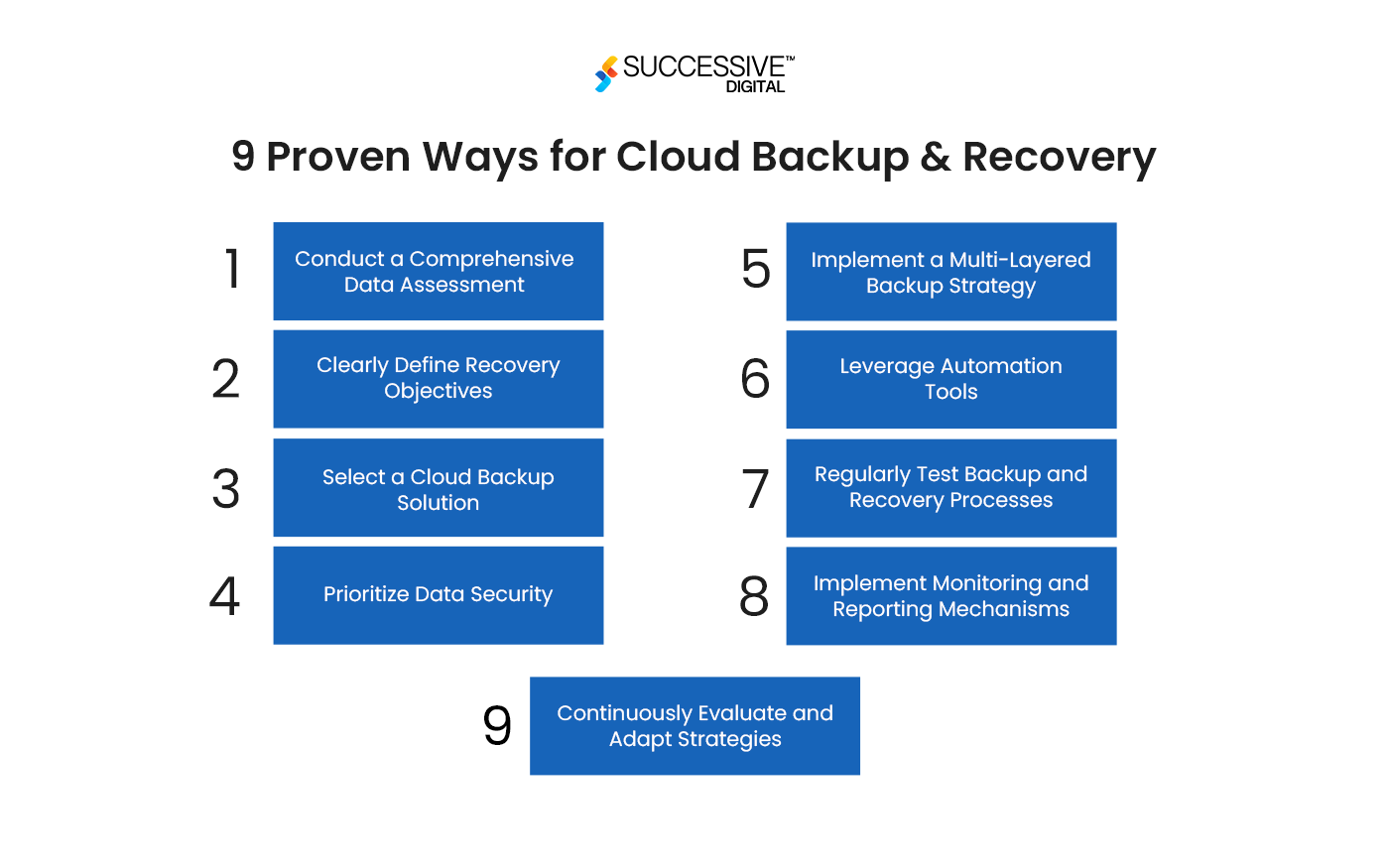
9 Proven Ways for Cloud Backup & Recovery
Now you know the types of cloud backup and when they can be utilized, let’s understand how to ensure backup and recovery while using the cloud:
-
Conduct a Comprehensive Data Assessment
It is imperative to have a complete understanding of your data landscape before implementing any backup and recovery strategy. To determine all of your organization’s essential data assets, do a thorough assessment. This covers information in the cloud, on-site, and across different systems and apps. Record the many kinds of data, their sources, consumption trends, and dependencies. This evaluation will yield important information about which data needs to be prioritized for backup and recovery operations.
-
Clearly Define Recovery Objectives
It is essential to set defined recovery objectives to ensure that your backup and recovery approach aligns with your business priorities and goals. The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) indicates the maximum allowable data loss in the event of an incident. In contrast, the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) establishes the maximum allowed downtime for your systems or services. Establishing RTOs and RPOs for various data and system types can efficiently customize your backup and recovery procedures to meet specific business continuity requirements.
-
Select a Cloud Backup Solution
Choosing the right cloud backup among many options requires careful thought, especially when integrating cloud consulting services. With so many cloud backup options, selecting the best one needs careful thought. When evaluating possible vendors, consider variables like data retention regulations, scalability, integration capabilities with your current infrastructure, compliance requirements, and reliability. To guarantee a simple and hassle-free experience, look for solutions that offer robust security features, automated backups, and seamless recovery alternatives.
-
Prioritize Data Security
Data security is an essential component of any backup and recovery plan. Use strong encryption techniques to safeguard your data from online dangers and unwanted access during transmission and storage. Implement access restrictions and authentication mechanisms to ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Audit and monitor access logs regularly to identify and address any possible security breaches quickly.
-
Implement a Multi-Layered Backup Strategy
Using a multi-layered plan to diversify your backup approach can help reduce the risk of data loss in various scenarios. This comprises cloud-based backups for scalability and accessibility, offsite backups for redundancy and disaster recovery, and onsite backups for instant access to vital data. By combining several backup techniques, complete data security and resistance against unforeseen damages are possible.
-
Leverage Automation Tools
Automation is essential for optimizing backup and recovery processes, cutting down on manual labor, and lowering the possibility of human error. Invest in technology and automation solutions that allow for automated failover mechanisms, incremental backups, and scheduled backups. Routine processes like data deduplication, integrity checks, and backup scheduling can be automated to increase efficiency and dependability and free up resources for other strategic objectives.
-
Regularly Test Backup and Recovery Processes
Regularly testing your backup and recovery processes is critical for validating their effectiveness and identifying any potential gaps or vulnerabilities. Conduct simulated disaster recovery drills and scenario-based testing to determine your organization’s level to face disruptions. Use these tests to assess backup integrity, recovery timescales, and system resilience. Use the knowledge gathered from testing exercises to refine and optimize your backup and recovery processes constantly.
-
Implement Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms
Proactive monitoring and reporting are essential parts of any backup and recovery plan. Set up monitoring tools to track the health and performance of your backup system in real-time. Monitor backup, storage consumption, network bandwidth, and system metrics to quickly detect discrepancies or performance concerns. Create reporting tools to produce regular reports on backup activity, recovery success rates, and compliance adherence.
-
Continuously Evaluate and Adapt Strategies
Evaluate the effectiveness of your current processes and technologies continuously in light of changing business requirements, regulatory changes, and emerging threats. Take stakeholder feedback, evaluate regularly, and stay current on industry best practices and developments. Use these insights to adjust and improve your backup and recovery plans, ensuring they remain effective and aligned with your organization’s goals.
Conclusion
When best practices are followed, cloud storage offers advantages such as scalability, flexibility, inexpensive storage costs, excellent data protection, and cyber-resilience. These best practices address three operations: backup, storage, and recovery. Smart system administrators consider the many sorts of data they need to secure. They also consider the monetary cost of backup, storage, and recovery and the time required for all three activities. Partnering with industry specialists can help you improve your data recovery capabilities. Collaborating with a cloud transformation company can bring significant insights, skills, and resources to help you preserve your data. The above-mentioned practices must be followed while utilizing the cloud for backup and recovery. If you have any queries, feel free to contact us!