Modernizing legacy systems in healthcare is necessary to take advantage of technological advancements and meet the changing needs of both patients and healthcare providers. It allows the incorporation of innovative technologies like AI/ML, which improve patient outcomes and diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, automating tasks, streamlining procedures, and enabling seamless data sharing among healthcare professionals increases operational efficiency.
Do you know that the application modernization services market size is projected to witness over 10% CAGR from 2023 to 2032, reaching USD 65 Billion? The reason why it is so widely accepted is because nearly half of the respondents noted cost reduction, improved integration with contemporary technologies, and more agility and flexibility.
Healthcare software modernization is expected to be driven mostly by enhancing security and efficiency, guaranteeing adherence to legal specifications, and protecting patient information.
In this blog, we will understand the importance of modernizing healthcare legacy systems, types of legacy healthcare systems, best practices for upgrading legacy medical systems, examples of healthcare legacy system modernization, and a set of challenges faced while using legacy systems.
Let’s explore further.
The Need for Modernizing Legacy Systems in Healthcare
To understand the need for IT modernization for healthcare facilities, it is important to know what legacy systems are. The healthcare system and software are outdated or are built using technologies that are no longer relevant. For example, using traditional EHR and EMR software does not receive updates or enhancements anymore.
Legacy systems may function as intended but become stagnant in growth and technology adoption for various reasons like vendor or technology discontinuation. As a result, using these systems is both risky and costly.
Therefore, healthcare systems modernization is crucial to ensure improved productivity and smooth workflow. No doubt, the global healthcare IT market is projected to grow at an impressive CAGR of 14.7% from 2024 to 2029, reaching US$834.35 billion by 2029.
Typically, legacy systems in healthcare handle vital organizational processes and data, and therefore, they are not easy to replace. However, they can lead to various challenges that are important to know so you can create the right digital transformation strategy to modernize legacy systems in healthcare.
Now, let’s understand the challenges of legacy medical systems.
What are the Challenges of Legacy Systems in Healthcare?
Legacy systems have been utilized in all the industries. Every legacy system has its own set of challenges. We are here to understand the challenges of legacy systems in healthcare:
Interoperability
The capacity of various software programs and healthcare systems to effortlessly share, interpret, and use data is known as interoperability. Integrating legacy systems with more modern technology and exchanging data across healthcare networks is challenging since these systems lack defined data formats and communication protocols.
Inefficient medical delivery, duplicate data entry, and fragmented patient information result from this lack of interoperability. Interoperability issues also impede continuity and coordination of treatment, which affects patient outcomes and safety.
Outdated User Interface
The user interfaces of legacy healthcare systems are often antiquated, complicated, and challenging to use. It’s possible that these interfaces don’t meet the changing requirements of healthcare professionals or comply with contemporary usability standards. With such issues, users can become frustrated, less productive, and resistant to embracing new technology.
Outdated user interfaces are a potential factor in mistakes, data entry delays, and decreased patient safety. Healthcare companies must prioritize user-centered design concepts and make modern interface investments to improve usability and user pleasure to overcome this obstacle.
Security Concerns
Healthcare organizations place a high priority on security since patient data is sensitive and cybersecurity attacks are becoming prevalent. In addition to frequently having weak security protections, legacy systems can be vulnerable to ransomware attacks, data breaches, and other security threats. These vulnerabilities could be caused by out-of-date software, weak encryption techniques, or insufficient access restrictions.
The risk of security breaches is further increased by the possibility that patches or security updates are not regularly applied to legacy systems. Healthcare companies need to put strong cybersecurity measures in place, like encryption, multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and frequent security audits, to reduce security risks.
Patient Engagement
To promote proactive healthcare management, patient satisfaction, and improved health outcomes, patient participation is essential. However, legacy systems do not have the patient engagement tools and capabilities necessary to enable patients to take an active role in their care.
Patients find it more difficult to make educated decisions about their health. These systems only provide restricted access to medical records, communication channels, or instructional materials.
Moreover, newer technologies make it easier to access healthcare services and information—like patient portals and mobile apps. Healthcare companies need to invest in upgrading their systems and promoting patient-centered treatment to improve patient engagement through interactive health management platforms, self-service tools, and tailored communication.
Data Silos
Data silos develop when information is kept in different systems or divisions of a company, making it difficult to access, exchange, and analyze data across the enterprise. Legacy systems lead to data silos because of their fragmented architecture and lack of interaction with other systems.
As a result, healthcare providers may struggle to gain a clear picture of patient data, resulting in incomplete or incorrect assessments of patient health status and treatment outcomes. Data silos also inhibit healthcare workers’ collaboration and efforts to use data analytics for clinical decision support, population health management, and quality improvement activities.
To solve data silos, healthcare companies must deploy data integration solutions, such as interoperable EHR systems, data warehouses, or health information exchanges, that aggregate and standardize data from several sources. Furthermore, organizations should have data governance rules and procedures to ensure data quality, security, and compliance throughout the organization.
These are a set of challenges that are frequently faced in legacy systems in healthcare. Now that the challenges are clear, it is time to introduce different types of legacy systems and why they need upgrades.
Types of Legacy Healthcare IT Systems
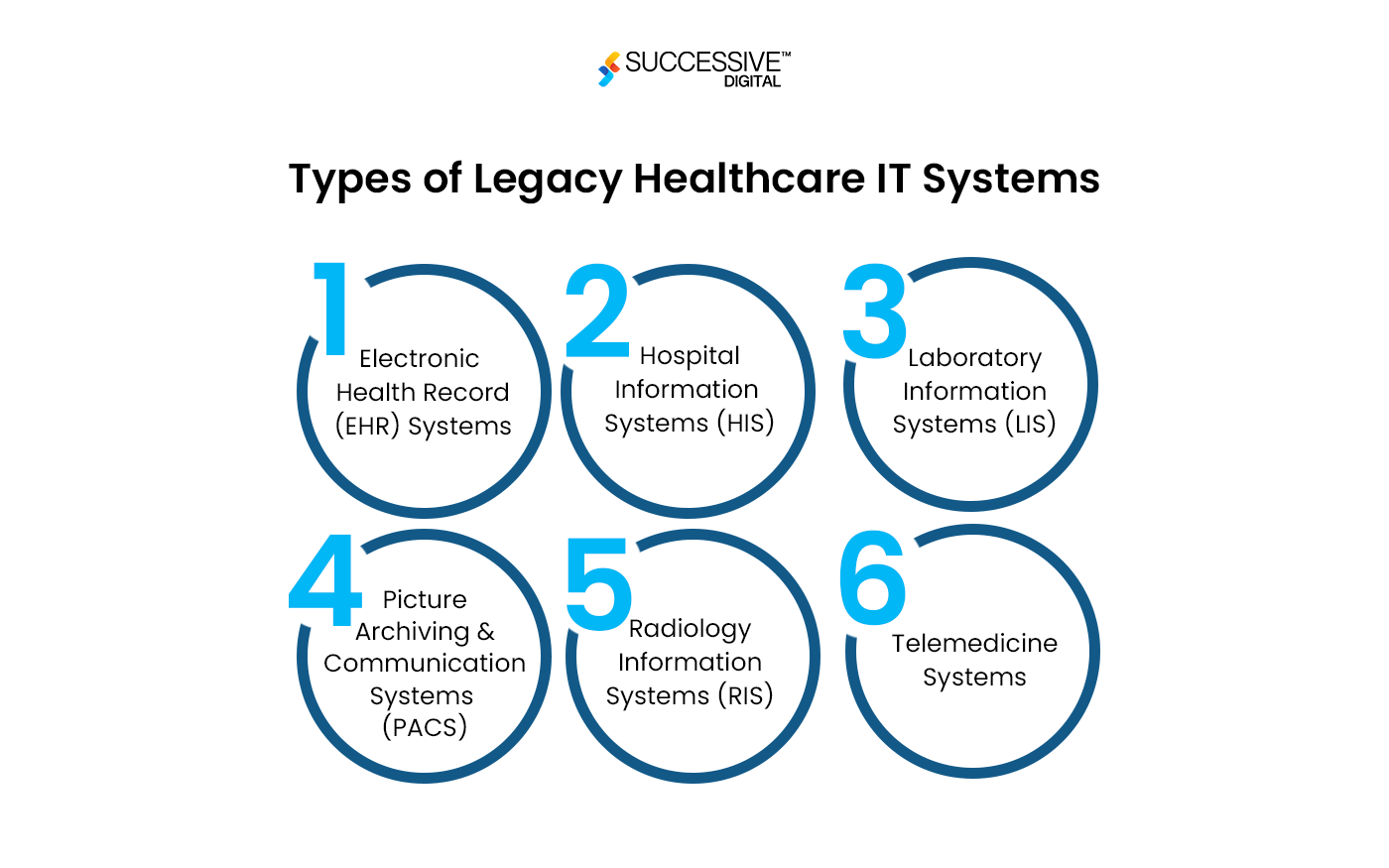
Legacy healthcare systems encompass a variety of healthcare software programs that were formerly utilized to assist various tasks within the healthcare industry. Below are the most known legacy healthcare IT systems:
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems
Early versions of EHR systems focused on keeping simple patient records. These systems eventually lack modern functionality, interoperability, and intuitive user interfaces. To embed advanced technologies, it’s imperative to modernize legacy systems in healthcare.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Legacy HIS includes systems for managing various administrative, financial, and clinical aspects of hospital operations. Outdated HIS systems struggle with interoperability, real-time data access, and reporting capabilities.
Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
These systems manage laboratory data, such as workflow and test results. Legacy LIS faces data standards concerns and a lack of integration capabilities with new diagnostic technology.
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS)
Legacy PACS primarily stores and retrieves medical images. Legacy systems have compatibility issues with advanced imaging technology and have low integration capabilities.
Radiology Information Systems (RIS)
RIS oversees radiological imaging workflows, scheduling, and invoicing. Older RIS lack features such as automatic appointment scheduling and have integration concerns with newer RIS.
Telemedicine Systems
Outdated telemedicine systems are among the legacy systems in the healthcare communications infrastructure. These healthcare systems must be improved to ensure secure communication and successful telehealth services.
Claims Processing Systems
This type of legacy system coordinate billing and reimbursement between payers and healthcare providers. The complexities of modern billing regulations and regulatory changes present a significant challenge to outdated claims processing systems.
Patient Engagement Systems
Modern solutions frequently have more user-friendly interfaces and functionalities than early patient engagement systems. To encourage patients to actively participate in their healthcare, these systems need to be updated.
As the healthcare industry changes, these outdated legacy systems in healthcare must be updated to meet the needs of data security, interoperability, and technological advancements.
Benefits of Modernizing Legacy Healthcare Systems
While legacy systems have served healthcare organizations well, they have various limitations. This can hinder growth, efficiency, and security. Therefore, upgrading to modern solutions is essential:
- Future-Ready Infrastructure
With healthcare software modernization, you can ensure your system is equipped with the latest technologies. Thus making it scalable and adaptable to future advancements.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs
Legacy systems often lead to costly upkeep. However, modernizing healthcare applications may require a significant budget, but it would be a one-time investment. In the long term, modern applications are likely to reduce maintenance expenses and technical debt.
Read our blog on Cloud FinOps to understand the cloud cost optimization process.
- Enhanced Security & Compliance
Older systems are more vulnerable to cyber threats. Modernizing ensures updated security protocols, better data protection, and compliance with evolving healthcare regulations.
- Improved Agility & Efficiency
Modern healthcare systems are highly advanced and effective in offering streamlined operations and enabling faster decision-making, leading to increased productivity.
- Higher Business Value & ROI
Upgraded systems optimize resource usage, reduce downtime, and improve service delivery, ultimately driving better financial and operational outcomes.
Let’s understand how you can modernize your legacy medical systems.
Approaches to Healthcare System Modernization
The healthcare application modernization methodology plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, security, and patient care. The best modernization strategy depends on the organization’s specific needs and goals.
Here are the top approaches:
Rehosting (“Lift and Shift”)
Moving existing applications to a new cloud environment with minimal changes, reducing infrastructure costs and improving scalability.
Replatforming (“Lift, Tinker, and Shift”)
Making minor modifications to optimize legacy applications for the cloud while maintaining core functionality.
Refactoring
Restructuring and optimizing code to improve performance, scalability, and security without changing core functionality.
Rearchitecting
Redesigning applications with cloud-native capabilities (e.g., microservices, serverless computing) to enhance efficiency and flexibility.
Rebuilding
Completely rewriting legacy applications from scratch using modern technologies to meet evolving business and regulatory needs.
Replacing
Retiring outdated systems and adopting off-the-shelf or SaaS solutions that offer better features, security, and compliance.
For seamless healthcare application development, following a multi-cloud environment strategy is ideal. Read the blog to know the benefits and challenges of this strategy for the healthcare industry.
Key Technologies for Healthcare System Modernization
It is essential to carefully select the latest technologies and frameworks for seamless healthcare software modernization. Here is the common tech stack used by modern digital transformation companies.
| Technology | Role in Modernization |
| Cloud Computing (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Enables scalable, cost-effective, and secure hosting of healthcare applications. |
| Microservices Architecture | Breaks down monolithic systems into smaller, independent services for flexibility and easier maintenance. |
| API Integration | Seamless data exchange between legacy and modern systems, improving interoperability. |
| Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning | Enhances diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized healthcare services. |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Automates repetitive tasks like billing, claims processing, and administrative workflows. |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Speeds up application development without extensive coding, enabling rapid deployment of healthcare solutions. |
| FHIR & HL7 Standards | Ensures standardized healthcare data exchange for improved interoperability. |
| DevOps & CI/CD Pipelines | Streamlines software updates, security patches, and deployment processes. |
| Cybersecurity & Compliance Tools | Strengthens data protection and ensures adherence to healthcare regulations. |
How to Modernize Legacy Medical Systems?
Modernizing legacy data systems in the healthcare industry entails taking calculated steps to improve and upgrade out-of-date healthcare systems while making sure they comply with emerging technologies and industry standards. The following are some of the most important actions in updating legacy healthcare systems:
Evaluation and Record-Keeping
Conduct a thorough analysis of the existing legacy systems, taking note of their dependability, functionality, and data formats. Record the precise integration specifications and objectives, keeping security and scalability in mind.
Specify Integration Goals
Clearly define your integration goals, such as improved data flow, increased functionality, or compliance with new technology. Align these with the goals of your healthcare company to ensure that the integration strategy benefits the broader business.
Choose an Integration Services
Choose an integration strategy based on the evaluated requirements and present infrastructure, such as data migration, APIs, middleware, or a combination of these alternatives. Consider the chosen method’s long-term viability and scalability to ensure that it meets the organization’s changing needs.
Integration of Middleware
When using middleware, make sure it can ease communication between modern applications and legacy systems. Configure middleware to provide a smooth data transfer and system interoperability.
API Integration
When using APIs, design or select ones that operate with both modern and legacy applications. To protect data during integration, make sure the appropriate authorization and authentication mechanisms are in place.
Data Migration
Plan and execute data transfer from existing legacy systems in healthcare infrastructure to the new environment. Check the data’s consistency and accuracy after migration.
Testing
Thoroughly test the interconnected systems to ensure that they function as intended. Conduct user acceptance, integration, and unit testing to identify and correct faults and malfunctions.
Implementation
To minimize disruptions to ordinary operations, choose a phased and progressive approach to integration. Monitor the integration process and address any issues that arise.
Monitoring and Optimization
Use monitoring tools to track user feedback and system performance. Continue to improve the linked systems to meet evolving business needs and user experiences.
By following these steps, you can effectively plan your modernization strategy and embed advanced technologies within your existing ecosystem. But when you need expert support, we are here to help.
How Can Successive Digital Help You Modernize Your Healthcare Legacy Systems?
Healthcare applications have the potential to transform patient care. Still, their success will be determined by how successfully they interact with the legacy systems that underpin most of the healthcare sector.
Despite the hurdles, modernizing outdated healthcare IT systems provides numerous benefits. As a result, the future of healthcare requires the cohabitation of legacy systems and technologies with the potential to improve patient outcomes and overall system efficacy.
As an Advanced AWS Consulting Partner, Successive Digital leverages its cloud infrastructure expertise and cutting-edge technologies. Our healthcare application modernization solutions are focused on supporting the seamless integration of advanced technologies with legacy systems, which continue to be the foundation of the healthcare industry.
Here’s a story of how we helped one of our client in modernizing their legacy system in healthcare.
Modernizing Legacy Medical Application for Effective Operations
A MedTech healthcare provider collaborated with Successive Digital to address key challenges in redefining the at-home screening experience through their App. The application initially faced issues with non-standard coding practices, inadequate adherence to medical regulations for patient data security, and inefficiencies in supporting new client onboarding and cross-functional team usage.
We swiftly modernized legacy applications by migrating them to AWS cloud infrastructure, enabling seamless day-to-day operations and remote at-home medical screening, especially vital during the COVID-19 pandemic. Their solutions included transforming the single-instance application into a multi-tier architecture, implementing robust security and compliance measures to support global expansion, and setting up scalable and fault-tolerant cloud infrastructure.
Additionally, we integrated the ADP marketplace as a new service, enhancing HEDIS quality. This case study exemplifies our expertise in delivering tailored healthcare solutions, emphasizing their proficiency in addressing complex challenges and driving innovation in the healthcare industry.
Conclusion
When it comes to scaling a business or gaining a competitive edge, an organization’s system or software can make all the difference in the modern digital age. This indicates that it is imperative to consider the software’s ability to adapt to changing business requirements. This is where a carefully considered modernization approach for legacy systems is beneficial.
Conclusively, healthcare software modernization will be a popular trend in 2025 and in the coming years.
Are you also struggling with outdated systems? We are here to help. Transform your legacy systems with us and turn your imagination into reality. Contact us Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
There are several benefits to modernizing healthcare legacy systems, and these benefits greatly improve patient care, operational effectiveness, and overall organizational performance. It makes it possible to incorporate modern technologies like machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), which can enhance patient monitoring, treatment programs, and diagnosis, producing better results and a more customized patient experience. Also, it results in increased operational efficiency and cost savings by streamlining workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and lowering administrative responsibilities.
By putting in place a few crucial steps, organizations can guarantee a smooth transition while modernizing healthcare legacy systems. First and foremost, thorough planning and strategy are crucial. This entails creating a complete roadmap that outlines objectives, schedules, resource allocation, and risk mitigation techniques while coordinating modernization activities with corporate goals. Using an iterative approach to modernization, it is possible to make small adjustments and change course in response to feedback and changing requirements.
Before starting the modernization process for legacy healthcare systems, several important considerations need to be made.
First and foremost, to pinpoint problems, constraints, and potential areas for development, a thorough evaluation of the current system is required. An examination of the integration difficulties, technological debt, and data integrity issues that must be resolved during modernization should be part of this assessment.
Second, it is crucial to make sure that healthcare standards, including HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA recommendations, are followed. Businesses need to think about how modernization projects may affect data security, privacy, and compliance requirements and build the appropriate safeguards into the project design.
Thirdly, it’s critical to ascertain the modernization project’s financial restrictions and resource availability.